SPARKS OF PRECISION
How EDM revolutionized the World of Manufacturing. Once discovered by pure chance, EDM has become one of the most important manufacturing technologies of our time and drives innovations in future technologies such as AI, electromobility, and aerospace
Text: Markus Huth
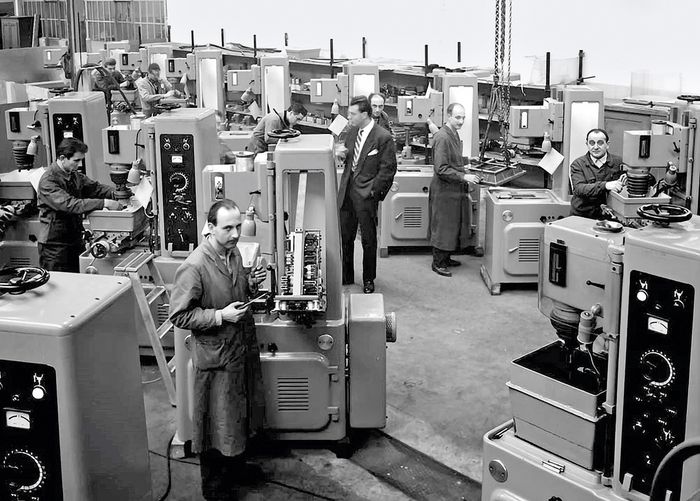
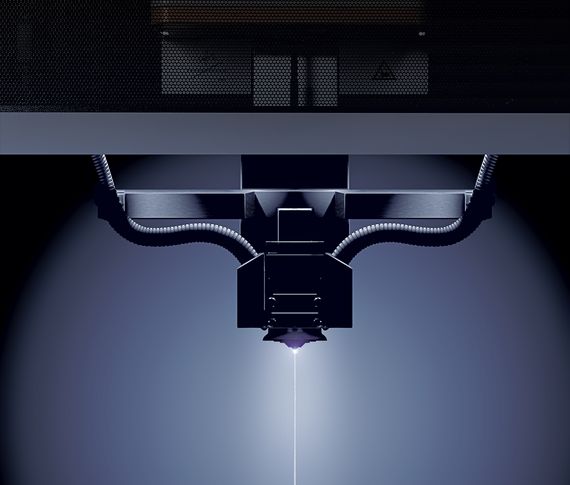
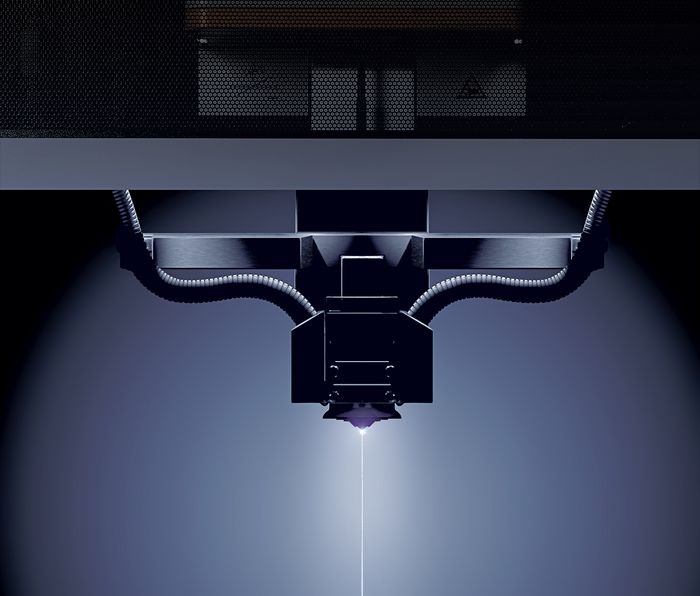
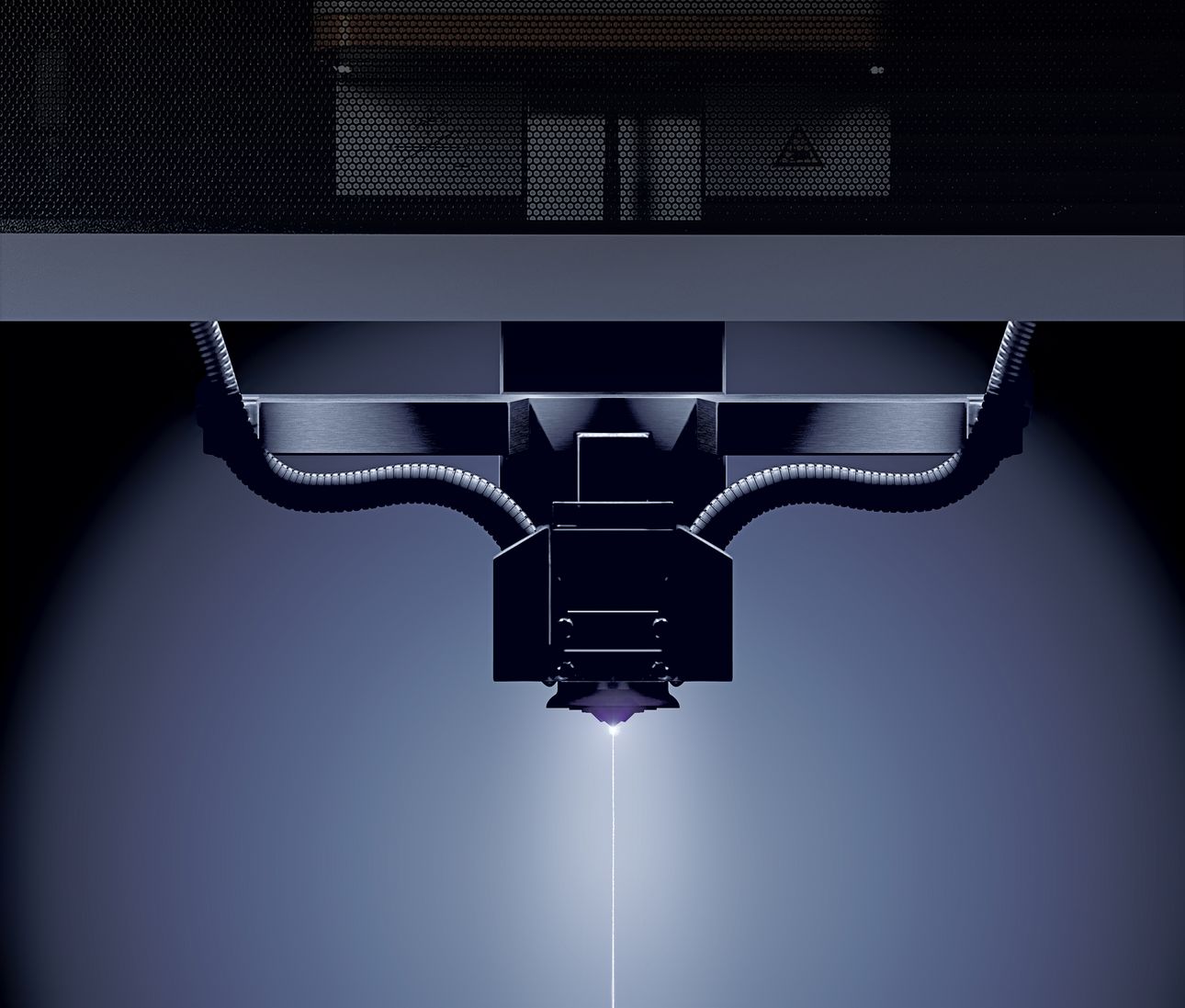



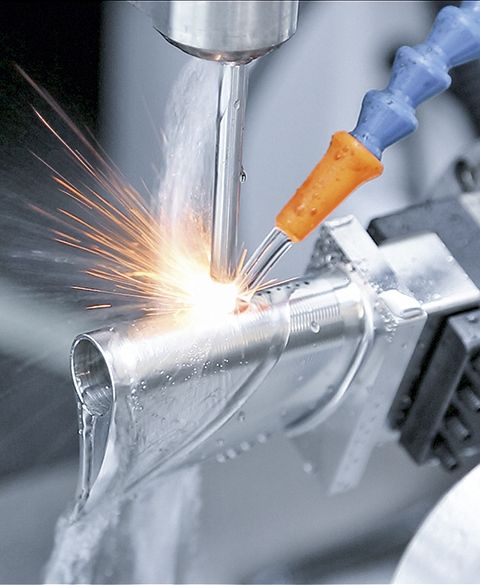
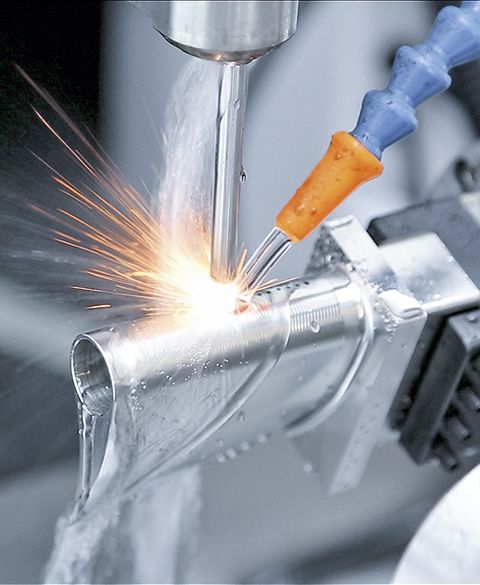
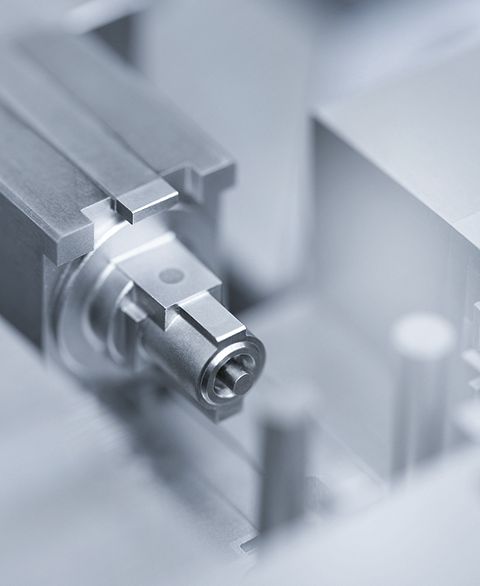
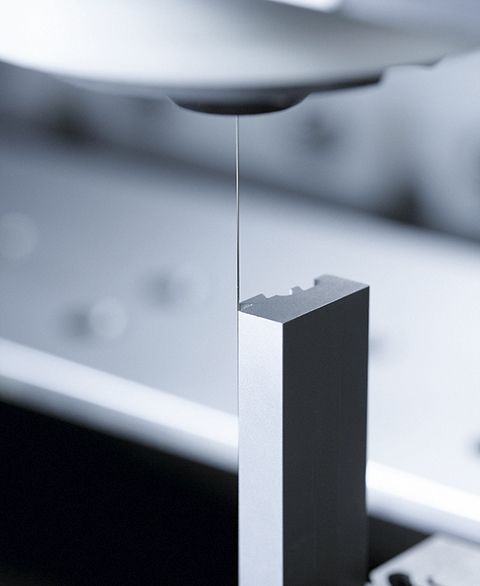
Fascinated, Russian scientists Boris and Natalya Lazarenko observe in their laboratory in Moscow in 1943 how spark discharges precisely remove metal. Actually, their experiment had aimed for the opposite, namely to reduce the damage to electrical contacts caused by spark formation. But shortly thereafter, they deliberately used the accidentally discovered effect for the first time to process materials – the birth of the modern manufacturing technology EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining). It works by igniting short, controlled sparks between an electrode and a conductive workpiece – embedded in a dielectric medium such as oil or deionized water. Each spark vaporizes microscopically small particles, while the fluid washes away deposits.
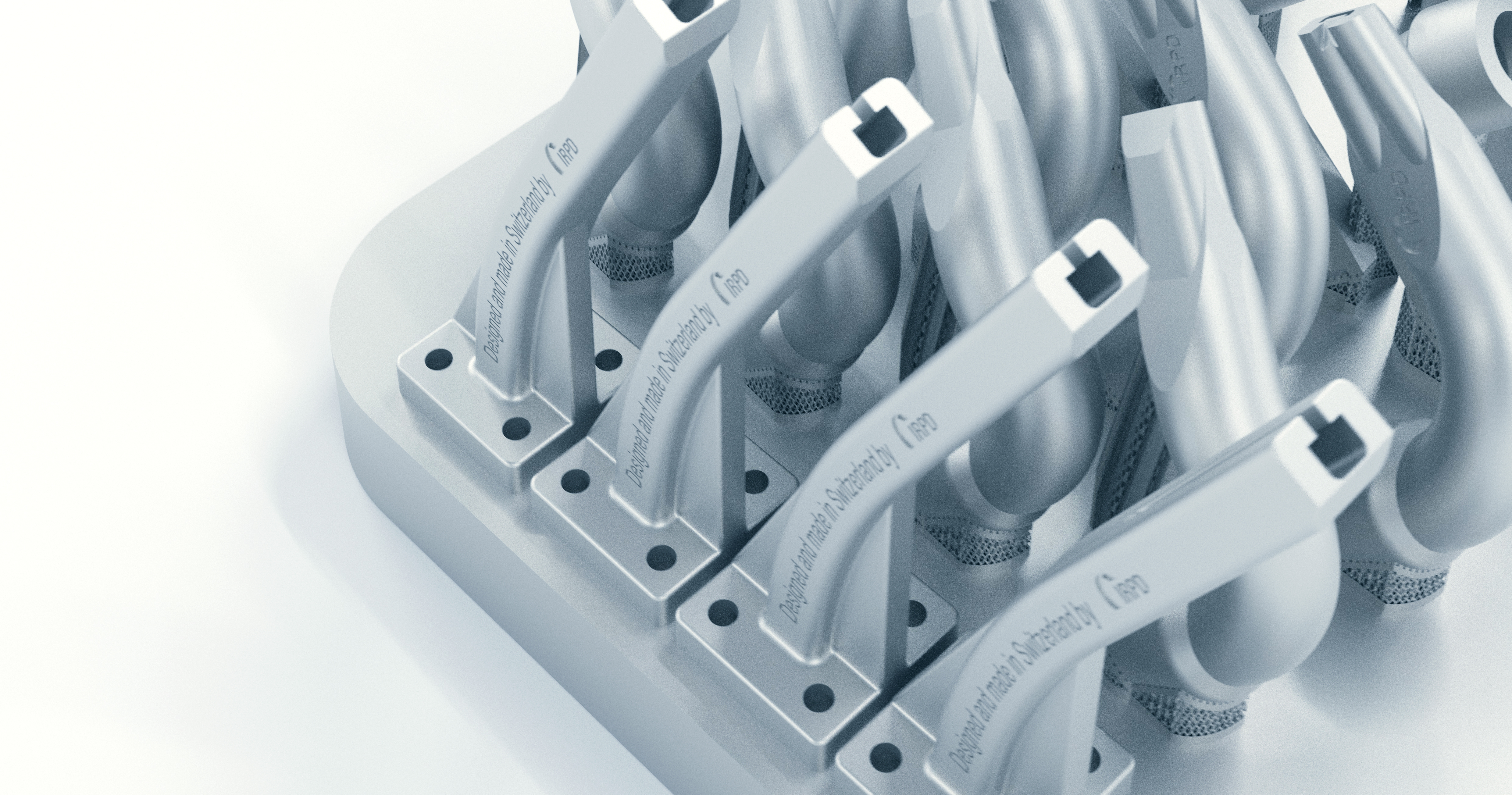
“You could compare it to a lightning strike that precisely carves away material, but this happens over a million times per second,” explains Umang Maradia, Head of TU EDM at UNITED MACHINING. This makes it possible to cut or shape even the hardest metals such as titanium alloys or tungsten carbide with micrometer precision. Unlike mechanical manufacturing technologies such as milling or grinding, this happens without contact. Especially for very fine and complex geometries in the micrometer range and hard materials, EDM is often the only efficient possibility for production. Another advantage is the excellent surface quality. Today, even molds for polished surfaces like plastic toy bricks or extreme precision molds for camera lenses can be produced via EDM. Additionally, it can excellently complement other processes such as milling, grinding, or lasers.
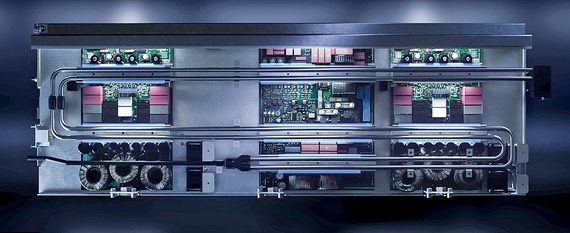

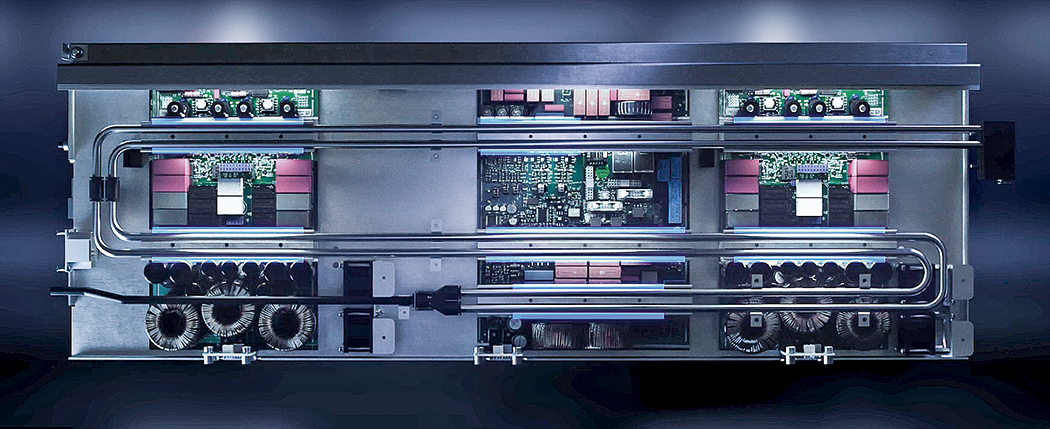
AGIE CHARMILLES SHAPES THE EDM INDUSTRY TO THIS DAY
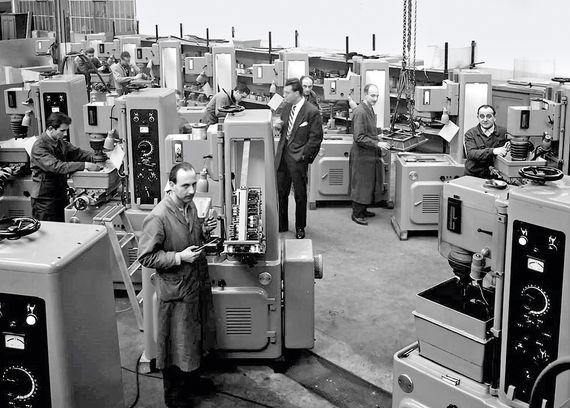
Shortly after the discovery in Russia, the development of EDM into an industry-viable manufacturing technology gained momentum in another country: In Switzerland, two companies – CHARMILLES and AGIE (A.G. for industrial electronics) – developed the first production-ready EDM machines and presented them to the world public at the machine tool exhibition in Milan in 1954. In the following decades, they also contributed numerous innovations to help realize the full potential of EDM. Today, both companies are part of UNITED MACHINING as AGIE CHARMILLES. “With over 1000 patents, we have shaped important standards in the industry and continue to do so,” says Maradia. Precisely controllable generators, automatic wire changers, coated wires, independent axis pairs, or AI-supported CNC control: the list of innovations is too long to enumerate them all here.
Today, EDM machines like the modern CUT- (for wire EDM), FORM- (for die-sinking EDM), and DRILL- (for hole-drilling EDM) series by AGIE CHARMILLES are high-tech devices. At their heart is the innovative Intelligent Power Generator (IPG), which allows fast, reliable, and digital control of each spark and drastically reduces energy consumption. The machines also support their users with smart features such as temperature control, automatic wire threading, sensor-supported real-time data acquisition, monitoring of spark concentration (Spark Track), intuitive operation (UNIQUA), and automation options. This means that they can meet the highest industry standards and produce numerous products for our modern world.
EDM TECHNOLOGIES
EDM IS A KEY TECHNOLOGY FOR THE FUTURE
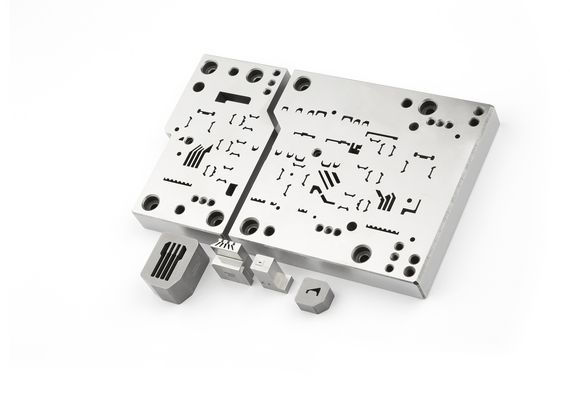

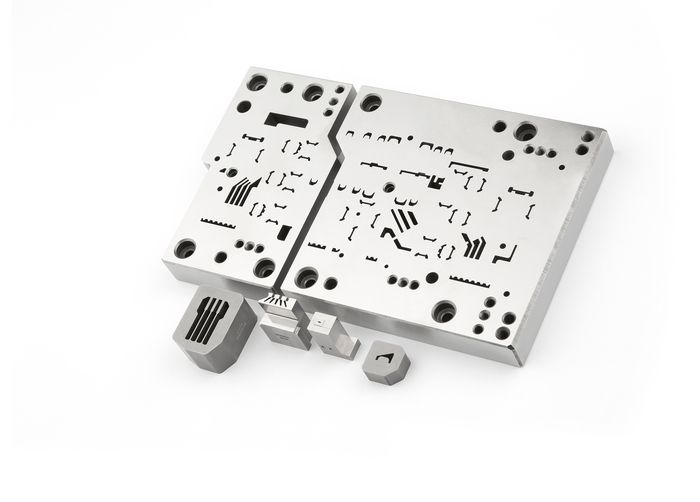
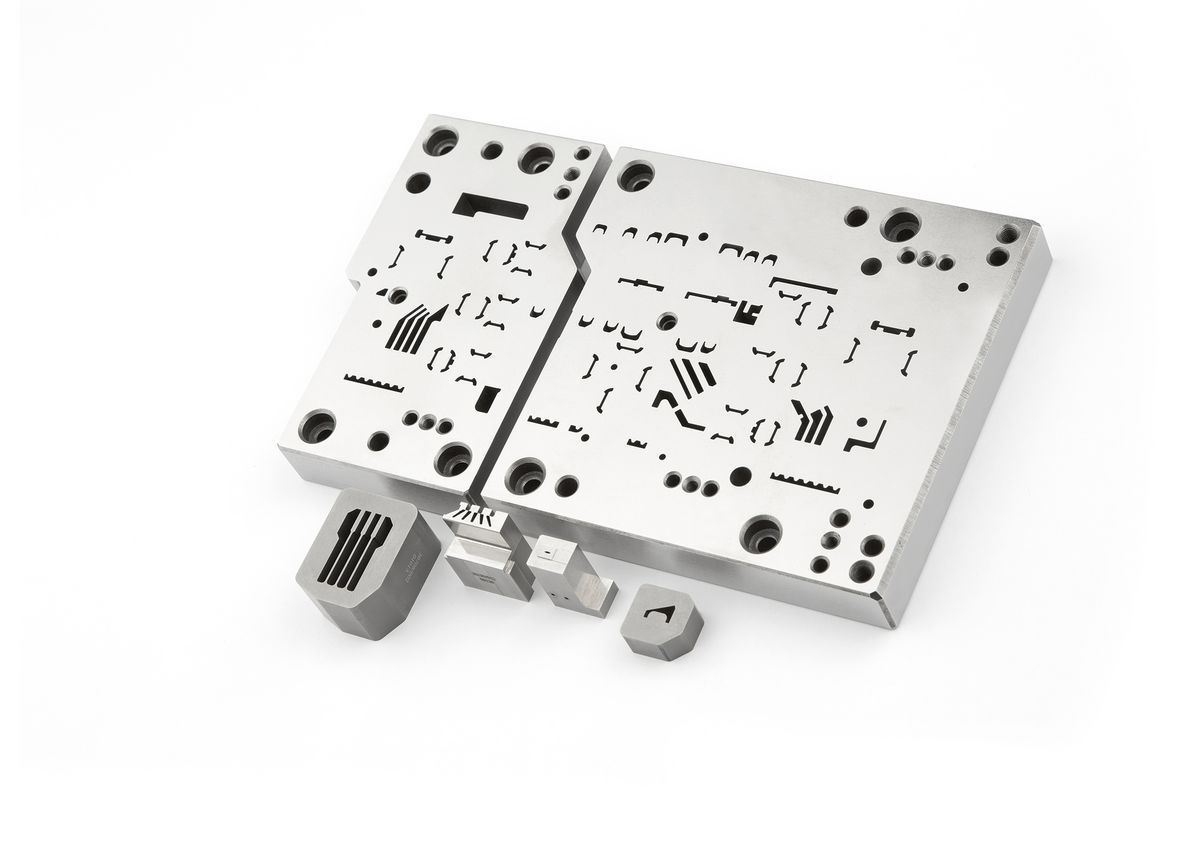
For example, EDM machines are used to produce the tools that manufacture the filigree data and energy connectors in electronics, whether for smartphones or data centers. The fine lamellae in electric motors or the complex geometries of fir tree slots in aircraft turbines are also manufactured with them. Another application area is injection molds for numerous plastic products of our daily lives, such as toothbrushes. “Whenever I open a yogurt, I have to think about EDM,” laughs Maradia. This is because the airtight sealing foils of the cups are punched with ultra-hard tungsten carbide tools. A CUT machine produces the razor-thin cutting edge with a precision of only a few micrometers, many times thinner than a human hair.
Experts expect that EDM as a manufacturing technology will become even more important in the future. This is because it enables the processing of highly complex geometries even in new high-tech materials, for example, in aerospace or automotive engineering, that would not be feasible with mechanical manufacturing methods. In addition, the trend toward miniaturization in electronics, medical technology, and energy systems continues and increases the demand for precision machining. “Thanks to digitalization and AI assistance, EDM machines will be even easier to automate in the future and will also be able to manufacture faster and with even more precision,” explains Maradia, adding: “EDM remains a backbone of our modern world.”